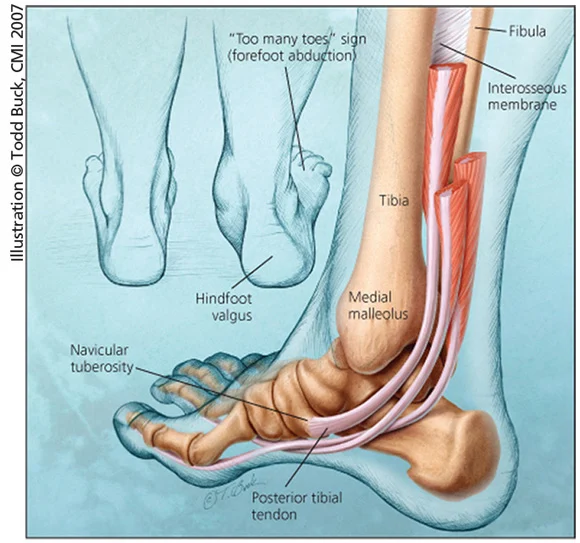
If you’re experiencing pain or swelling along the inside of your ankle or arch, you may be dealing with tibialis posterior tendon pain. This tendon plays a crucial role in supporting the arch of your foot and stabilizing your ankle. When it becomes inflamed or damaged, everyday activities like walking, running, or standing can become uncomfortable.
What Is the Tibialis Posterior Tendon?
The tibialis posterior tendon connects the calf muscles to the bones on the inside of the foot. Its main function is to support the arch and help with movements such as walking, pushing off the ground, and balancing.
When this tendon is strained or injured, the condition is often called posterior tibial tendon dysfunction (PTTD) or tibialis posterior tendinopathy.
Common Causes of Tibialis Posterior Pain
• Overuse injuries from running, walking long distances, or high-impact sports
• Flat feet or fallen arches, which put extra strain on the tendon
• Sudden injuries, such as twisting the ankle
• Age-related wear and tear, as the tendon weakens over time
• Obesity or weight gain, which increases pressure on the tendon
Symptoms of Tibialis Posterior Problems
You may have tibialis posterior tendon pain if you notice:
• Pain and swelling along the inside of the ankle and foot
• Discomfort that worsens with activity and improves with rest
• Difficulty standing on tiptoe or pushing off the foot
• Flattening of the arch (in advanced cases)
• Ankle weakness or instability
Home Remedies That May Help
If your symptoms are mild, you may find some relief with:
• Rest and ice: Reduce activity and apply ice packs for 15–20 minutes.
• Supportive footwear: Wear shoes with good arch support and cushioning.
• Orthotic insoles: Over-the-counter arch supports can help reduce strain.
• Elevation and compression: To help manage swelling.
⚠️ Avoid pushing through pain. Continuing activity with tendon pain can lead to long-term damage.
Professional Treatment for Tibialis Posterior Pain
If pain persists, a podiatrist can provide targeted treatments, such as:
• Custom orthotics to support the arch and offload pressure from the tendon
• Strapping or bracing to stabilize the ankle
• Physiotherapy exercises to strengthen and stretch the tendon
• Shockwave therapy for stubborn tendon pain
• Referral for imaging tests (ultrasound or MRI) if a tear is suspected
In severe cases where the tendon is torn or significantly damaged, surgical intervention may be considered.
When to See a Podiatrist
You should book an appointment if:
• The pain is persistent or worsening
• Swelling or tenderness around the ankle continues despite rest
• You notice flattening of your arch or changes in foot shape
• Walking, running, or daily activities are becoming difficult
The Bottom Line
Tibialis posterior tendon pain can significantly affect mobility if left untreated. Early diagnosis and treatment from a podiatrist can relieve pain, protect your arch, and prevent long-term complications.